In the previous article, a member of the Performance Management examining team revealed all about The Goal, the book in which the theory of constraints and throughput accounting were introduced in the context of a novel. In this second article, she sets out the five focusing steps of the theory of constraints, briefly explaining each one and then will go through two examples showing you how these steps might be applied in practice or in exam questions. It’s worth noting at this stage that, while the theory of constraints and throughput accounting were introduced in The Goal, they were further developed by Goldratt later.
The five focusing steps
The theory of constraints is applied within an organisation by following what are called ‘the five focusing steps.’ These are a tool that Goldratt developed to help organisations deal with constraints, otherwise known as bottlenecks, within the system as a whole (rather than any discrete unit within the organisation.) The steps are as follows:
Step 1: Identify the system’s bottlenecks
Often, in exam questions, you will be told what the bottleneck resource is. If not, it is usually quite simple to work out. For example, let’s say that an organisation has market demand of 50,000 units for a product that goes through three processes: cutting, heating and assembly. The total time required in each process for each product and the total hours available are:

The total time required to make 50,000 units of the product can be calculated and compared to the time available in order to identify the bottleneck.
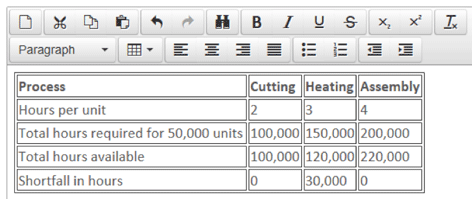
It is clear that the heating process is the bottleneck. The organisation will in fact only be able to produce 40,000 units (120,000/3) as things stand.
Step 2: Decide how to exploit the system’s bottlenecks
This involves making sure that the bottleneck resource is actively being used as much as possible and is producing as many units as possible. So, ‘productivity’ and ‘utilisation’ are the key words here. In ‘The Goal’, Alex noticed that the NCX 10 was sometimes dormant and immediately changed this by making sure that set ups took place before workers went on breaks, so that the machines were always left running. Similarly, the furnaces were sometimes left idle for extended periods before the completed parts were unloaded and new parts were put in. This was because workers were being called away to work on non-bottleneck machines, rather than being left standing idle while waiting for the furnaces to heat the parts. This was addressed by making sure that there were always workers at the furnaces, even if they had nothing to do for a while.
Step 3: Subordinate everything else to the decisions made in Step 2
The main point here is that the production capacity of the bottleneck resource should determine the production schedule for the organisation as a whole. Remember how, in the previous article, I talked about how new bottlenecks seemed to be appearing at the UniCo plant, because non-bottleneck machines were producing more parts than the bottleneck resources could absorb? Idle time is unavoidable and needs to be accepted if the theory of constraints is to be successfully applied. To push more work into the system than the constraint can deal with results in excess work-in-progress, extended lead times, and the appearance of what looks like new bottlenecks, as the whole system becomes clogged up. By definition, the system does not require the non-bottleneck resources to be used to their full capacity and therefore they must sit idle for some of the time.
Step 4: Elevate the system’s bottlenecks
In The Goal, Alex was initially convinced that there was no way to elevate the capacities of the NCX 10 machine and the furnace without investing in new machinery, which was not an option. Jonah made him and his team think about the fact that, while the NCX 10 alone performed the job of three of the old machines, and was very efficient at doing that job, the old machines had still been capable of producing parts. Admittedly, the old machines were slower but, if used alongside the NCX 10, they were still capable of elevating production levels. Thus, one of Alex’s staff managed to source some of these old machines from one of UniCo’s sister plants; they were sitting idle there, taking up factory space, so the manager was happy not to charge Alex’s plant for the machines. In this way, one of the system’s bottlenecks was elevated without requiring any capital investment.
This example of elevating a bottleneck without cost is probably unusual. Normally, elevation will require capital expenditure. However, it is important that an organisation does not ignore Step 2 and jumps straight to Step 4, and this is what often happens. There is often untapped production capacity that can be found if you look closely enough. Elevation should only be considered once exploitation has taken place.
Step 5: If a new constraint is broken in Step 4, go back to Step 1, but do not let inertia become the system’s new bottleneck
When a bottleneck has been elevated, a new bottleneck will eventually appear. This could be in the form of another machine that can now process less units than the elevated bottleneck. Eventually, however, the ultimate constraint on the system is likely to be market demand. Whatever the new bottleneck is, the message of the theory of constraints is: never get complacent. The system should be one of ongoing improvement because nothing ever stands still for long.
I am now going to have a look at an example of how a business can go about exploiting the system’s bottlenecks – ie using them in a way so as to maximise throughput. In practice, there may be lots of options open to the organisation such as the ones outlined in The Goal. In the context of an exam question, however, you are more likely to be asked to show how a bottleneck can be exploited by maximising throughput via the production of an optimum production plan. This requires an application of the simple principles of key factor analysis, otherwise known as limiting factor analysis or principal budget factor.
Limiting factor analysis and throughput accounting
Once an organisation has identified its bottleneck resource, as demonstrated in Step 1 above, it then has to decide how to get the most out of that resource. Given that most businesses are producing more than one type of product (or supplying more than one type of service), this means that part of the exploitation step involves working out what the optimum production plan is, based on maximising throughput per unit of bottleneck resource.
In key factor analysis, the contribution per unit is first calculated for each product, then a contribution per unit of scarce resource is calculated by working out how much of the scarce resource each unit requires in its production. In a throughput accounting context, a very similar calculation is performed, but this time it is not contribution per unit of scarce resource which is calculated, but throughput return per unit of bottleneck resource.
Throughput is calculated as ‘selling price less direct material cost.’ This is different from the calculation of ‘contribution’, in which both labour costs and variable overheads are also deducted from selling price. It is an important distinction because the fundamental belief in throughput accounting is that all costs except direct materials costs are largely fixed – therefore, to work on the basis of maximising contribution is flawed because to do so is to take into account costs that cannot be controlled in the short term anyway. One cannot help but agree with this belief really since, in most businesses, it is simply not possible, for example, to hire workers on a daily basis and lay workers off if they are not busy. A workforce has to be employed within the business and available for work if there is work to do. You cannot refuse to pay a worker if he is forced to sit idle by a machine for a while.
Example 1
Beta Co produces 3 products, E, F and G all in the same factory, details of which are shown below:

There are 320,000 bottleneck hours available each month.
Required:
Calculate the optimum product mix each month.
Solution:
A few simple steps can be followed:
- Calculate the throughput per unit for each product.
- Calculate the throughput return per hour of bottleneck resource.
- Rank the products in order of the priority in which they should be produced, starting with the product that generates the highest return per hour first.
- Calculate the optimum production plan, allocating the bottleneck resource to each one in order, being sure not to exceed the maximum demand for any of the products.
It is worth noting here that you often see another step carried out between Steps 2 and 3 above. This is the calculation of the throughput accounting ratio for each product. Thus far, ratios have not been discussed, and while I am planning on mentioning them later, I have never seen the point of inserting this extra step in when working out the optimum production plan for products all made in the same factory. The ranking of the products using the return per factory hour will always produce the same ranking as that produced using the throughput accounting ratio, so it doesn’t really matter whether you use the return or the ratio. This is because the cost per factory hour (the denominator of the throughput accounting ratio) will be the same for all the products.
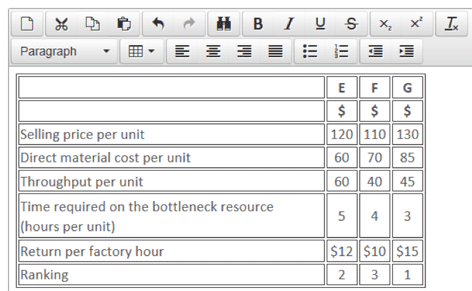
It is worth noting that, before the time taken on the bottleneck resource was taken into account, product E appeared to be the most profitable because it generated the highest throughput per unit. However, applying the theory of constraints, the system’s bottleneck must be exploited by using it to produce the products that maximise throughput per hour first (Step 2 of the five focusing steps). This means that product G should be produced in priority to E.
In practice, Step 3 will be followed by making sure that the optimum production plan is adhered to throughout the whole system, with no machine making more units than can be absorbed by the bottleneck, and sticking to the priorities decided.
When answering a question like this in an exam it is useful to draw up a small table, like the one shown below. This means that the marker can follow your logic and award all possible marks, even if you have made an error along the way.
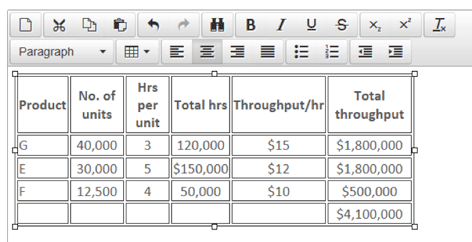
Each time you allocate time on the bottleneck resource to a product, you have to ask yourself how many hours you still have available. In this example, there were enough hours to produce the full quota for G and E. However, when you got to F, you could see that out of the 320,000 hours available, 270,000 had been used up (120,000 + 150,000), leaving only 50,000 hours spare.
Therefore, the number of units of F that could be produced was a balancing figure – 50,000 hours divided by the four hours each unit requires – ie 12,500 units.
The above example concentrates on Steps 2 and 3 of the five focusing steps. I now want to look at an example of the application of Steps 4 and 5. I have kept it simple by assuming that the organisation only makes one product, as it is the principle that is important here, rather than the numbers. The example also demonstrates once again how to identify the bottleneck resource (Step 1) and then shows how a bottleneck may be elevated, but will then be replaced by another. It also shows that it may not always be financially viable to elevate a bottleneck.
Example 2:
Cat Co makes a product using three machines – X, Y and Z. The capacity of each machine is as follows:

The demand for the product is 1,000 units per week. For every additional unit sold per week, net present value increases by $50,000. Cat Co is considering the following possible purchases (they are not mutually exclusive):
Purchase 1: Replace machine X with a newer model. This will increase capacity to 1,100 units per week and costs $6m.
Purchase 2: Invest in a second machine Y, increasing capacity by 550 units per week. The cost of this machine would be $6.8m.
Purchase 3: Upgrade machine Z at a cost of $7.5m, thereby increasing capacity to 1,050 units.
Required:
Which is Cat Co’s best course of action?
Solution:
First, it is necessary to identify the system’s bottleneck resource. Clearly, this is machine Z, which only has the capacity to produce 500 units per week. Purchase 3 is therefore the starting point when considering the logical choices that face Cat Co. It would never be logical to consider either Purchase 1 or 2 in isolation because of the fact that neither machines X nor machine Y is the starting bottleneck. Let’s have a look at how the capacity of the business increases with the choices that are available to it.

From the table above, it can be seen that once a bottleneck is elevated, it is then replaced by another bottleneck until ultimately market demand constrains production. At this point, it would be necessary to look beyond production and consider how to increase market demand by, for example, increasing advertising of the product.
In order to make a decision as to which of the machines should be purchased, if any, the financial viability of the three options should be calculated.

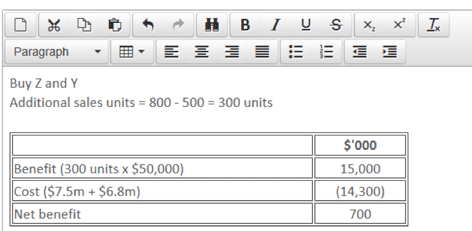

The company should therefore invest in all three machines if it has enough cash to do so.
The example of Cat Co demonstrates the fact that, as one bottleneck is elevated, another one appears. It also shows that elevating a bottleneck is not always financially viable. If Cat Co was only able to afford machine Z, it would be better off making no investment at all because if Z alone is invested in, another bottleneck appears too quickly for the initial investment cost to be recouped.
Ratios
I want to finish off by briefly mentioning throughput ratios. There are three main ratios that are calculated: (1) return per factory hour, (2) cost per factory hour and (3) the throughput accounting ratio.
1. Return per factory hour = Throughput per unit / product time on bottleneck resource.
As we saw in Example 1, the return per factory hour needs to be calculated for each product.
2. Cost per factory hour = Total factory costs / total time available on bottleneck resource.
The ‘total factory cost’ is simply the ‘operational expense’ of the organisation referred to in the previous article. If the organisation was a service organisation, we would simply call it ‘total operational expense’ or something similar. The cost per factory hour is across the whole factory and therefore only needs to be calculated once.
3. Throughput accounting ratio (TPAR) = Return per factory hour/cost per factory hour.
In any organisation, you would expect the throughput accounting ratio to be greater than 1. This means that the rate at which the organisation is generating cash from sales of this product is greater than the rate at which it is incurring costs. It follows on, then, that if the ratio is less than 1, this is not the case, and changes need to be made quickly.
Conclusion
At this point, I’m hopeful that you are now looking forward to reading The Goal as soon as possible and that you have a better understanding of the theory of constraints and throughput accounting, which you can put into practice by tackling some questions.
Written by a member of the Performance Management examining team


